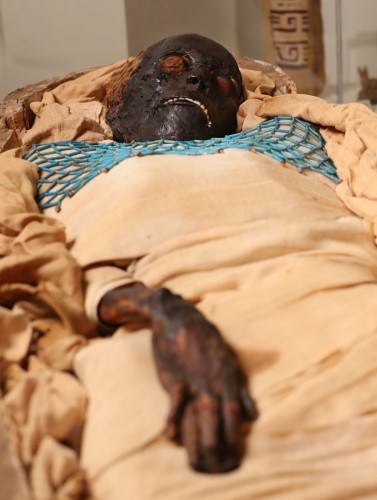
Takabuti, the famous ancient Egyptian mummy on display at the Ulster Museum, suffered a violent death from a knife attack, a team of experts from National Museums NI, University of Manchester, Queen’s University Belfast and Kingsbridge Private Hospital have revealed.
The team, whose findings are made public on the 185 year anniversary of Takabuti’s unwrapping in 1835, also show that her DNA is more genetically similar to Europeans rather than modern Egyptian populations.
The team show Takabuti had an extra tooth – 33 instead of 32 – something which only occurs in 0.02% of the population and an extra vertebrae, which only occurs 2% of the population.
And Takabuti’s heart, previously thought to have been missing, was identified by the state of the art technology used by the researchers as intact and perfectly preserved.
The scientific team consisted of Professor Rosalie David, Drs Bart van Dongen, Konstantina Drosou, Sharon Fraser, Professor Tony Freemont, Ds Roger Forshaw, Robert Loynes and Keith White from The University of Manchester
It also included Professors Eileen Murphy and Paula Reimar from Belfast University; Professor Caroline Wilkinson and Dr Sarah Shrimpton from Liverpool John Moores University; and Dr David Tosh from the Ulster Museum.
The scans show she was stabbed in the upper back near her left shoulder and that it was the cause of her death.
The findings finally solve the mystery of the mummy which has intrigued Egyptologists – and the public – since she was first unwrapped in Belfast in 1835. It transforms our understanding of Takabuti’s life in ancient Egypt and her journey into the afterlife.
The project was supported by funding from Friends of the Ulster Museum. Kingsbridge Private Hospital facilitated the work by providing their expertise and use of a portable x-ray machine to aid sampling for DNA work.
According to the team, the mysterious object in her body cavity, previously thought to be her heart, was in fact material used to pack the knife wound.
Takabuti lived over 2,600 years ago and died in her 20s. Experts say she was probably a married woman because she was a leading woman living – or mistress – who lived in a Thebes house – where Luxor is today.
She was acquired in Thebes by Thomas Greg from Holywood, County Down and brought to Belfast in 1834.
Dr Greer Ramsey, Curator of Archaeology at National Museums NI, says advances in scientific techniques have made the new findings possible.
He said: “There is a rich history of testing Takabuti since she was first unwrapped in Belfast in 1835. But in recent years she has undergone x-rays, CT scans, hair analysis and radio carbon dating. The latest tests include DNA analysis and further interpretations of CT scans which provides us with new and much more detailed information.
“The significance of confirming Takabuti’s heart is present cannot be underestimated as in ancient Egypt this organ was removed in the afterlife and weighed to decide whether or not the person had led a good life. If it was too heavy it was eaten by the demon Ammit and your journey to the afterlife would fail.”
The tests and examination of Takabuti were carried out over a period of months by the team using the latest scanning technologies, leading to new insights into Egyptian high society in the 25th dynasty.
Professor Rosalie David, an Egyptologist from The University of Manchester said: “This study adds to our understanding of not only Takabuti, but also wider historical context of the times in which she lived: the surprising and important discovery of her European heritage throws some fascinating light on a significant turning-point in Egypt’s history.
“This study, which used cutting-edge scientific analysis of an ancient Egyptian mummy – demonstrates how new information can be revealed thousands of years after a person’s death. Our team – drawn from institutions and specialisms – was in a unique position to provide the necessary expertise and technology for such a wide-ranging study.”