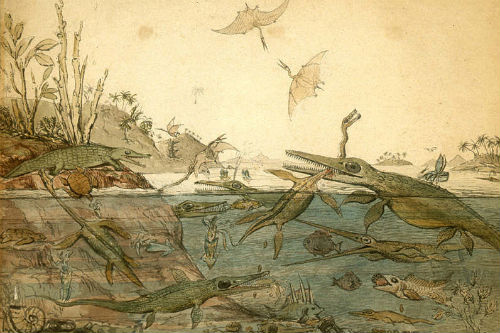
While dinosaurs ruled the land in the Mesozoic, the oceans were filled by predators such as crocodiles and giant lizards, but also entirely extinct groups such as ichthyosaurs and plesiosaurs.
Now for the first time, researchers at the University of Bristol have modelled the changing ecologies of these great sea dragons.
Mesozoic oceans were unique in hosting diverse groups of fossil reptiles, many of them over 10 metres long.
These toothy monsters fed on a variety of fishes, molluscs, and even on each other. Yet most had disappeared by the end of the Cretaceous, 66 million years ago, when the dinosaurs also died out. There are still some marine crocodiles, snakes and turtles today, but sharks, seals, and whales took over these ecological roles.
In a new study, completed when she was studying for the MSc in Palaeobiology at the University of Bristol’s School of Earth Sciences, Jane Reeves, now a PhD student at the University of Manchester used modern computational methods to explore how all these marine reptiles divided up the spoils.
Jane said: “It’s difficult to work out the ecology and function of fossil animals but we decided to focus mainly on their feeding and swimming styles. I tracked down information on 371 of the best-known Mesozoic marine tetrapods, and coded each one for 35 ecological traits, including body size, diet, likely hunting style, tooth type, presence or absence of armour, limb shape and habitat.”
The numerical analysis showed that all these marine reptiles could be divided into just six ecological categories linking how they moved, where they lived, and how they fed: pursuit predators that chased their prey, ambush predators that lurked and waited for the prey to swim past (two groups, one in deep water, one in shallow), a fourth group of reptiles that could still walk on land, shallow-water shell-crushers and foragers, and marine turtles with a variety of life modes.
Professor Mike Benton, who co-supervised the study, said: “A problem with studies of form and function of fossils is that we have to be careful in reconstructing the behaviour of ancient animals. But in Jane’s study, she used ecological characters from the start where their function had already been established. For example, sharp pointy teeth mean fish-eating, whereas broad, flat teeth mean shell crushing.”